Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
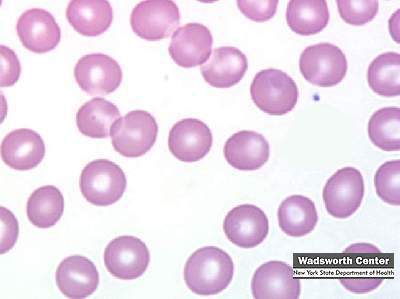
The mature red blood cell (rbc) consists primarily of hemoglobin (about 90%). The membrane is composed of lipids and proteins. In addition, there are numerous enzymes present which are necessary for oxygen transport and cell viability. The main function of the red cell is to carry oxygen to the tissues and return carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. The protein hemoglobin is responsible for most of this exchange. Normal red blood cells are round, have a small area of central pallor, and show only a slight variation in size. A normal red cell is 6-8 µm in diameter. As the relative amount of hemoglobin in the red cell decreases or increases, the area of central pallor will decrease or increase accordingly.
|
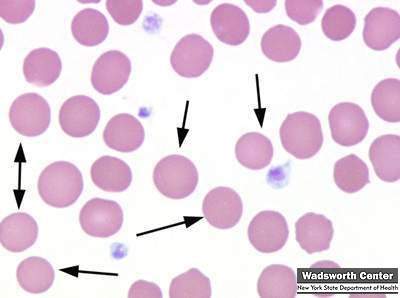
Spherocytes
Spherocytes are red blood cells that are almost spherical in shape. They have no area of central pallor like a normal red blood cell. Large spherocytes (macrospherocytes) are seen in hemolytic anemia. Small spherocytes (microspherocytes) are sometimes seen in severe burn cases. A variety of spherical forms are seen in hereditary spherocytosis. The cells depicted in this image are from a patient with hereditary spherocytosis.
|
My Blood
My mother has been diagnosed with Spherocytosis, also called Hereditary Spherocytic Hemolytic Anemia. I am at increased risk for having the condition as well. Due to a history over many years of blood donations of being near the lower boundary for 'normal' blood iron levels for men (13.5 gm), I practice a daily regimen of taking a multivitamin tablet with minerals; this provides 18 mg of iron in addition to that which comes with my regular diet. For the few days prior to a blood donation, I often take two tablets per day.
In February 2001, after taking two iron fortified vitamin tablets per day for three days, I was deferred as a blood donor for having 13.3 gm Hbg. Consequently, I had some of my blood put under a microscope to see what condition my red blood cells looked like. The image below is the result.
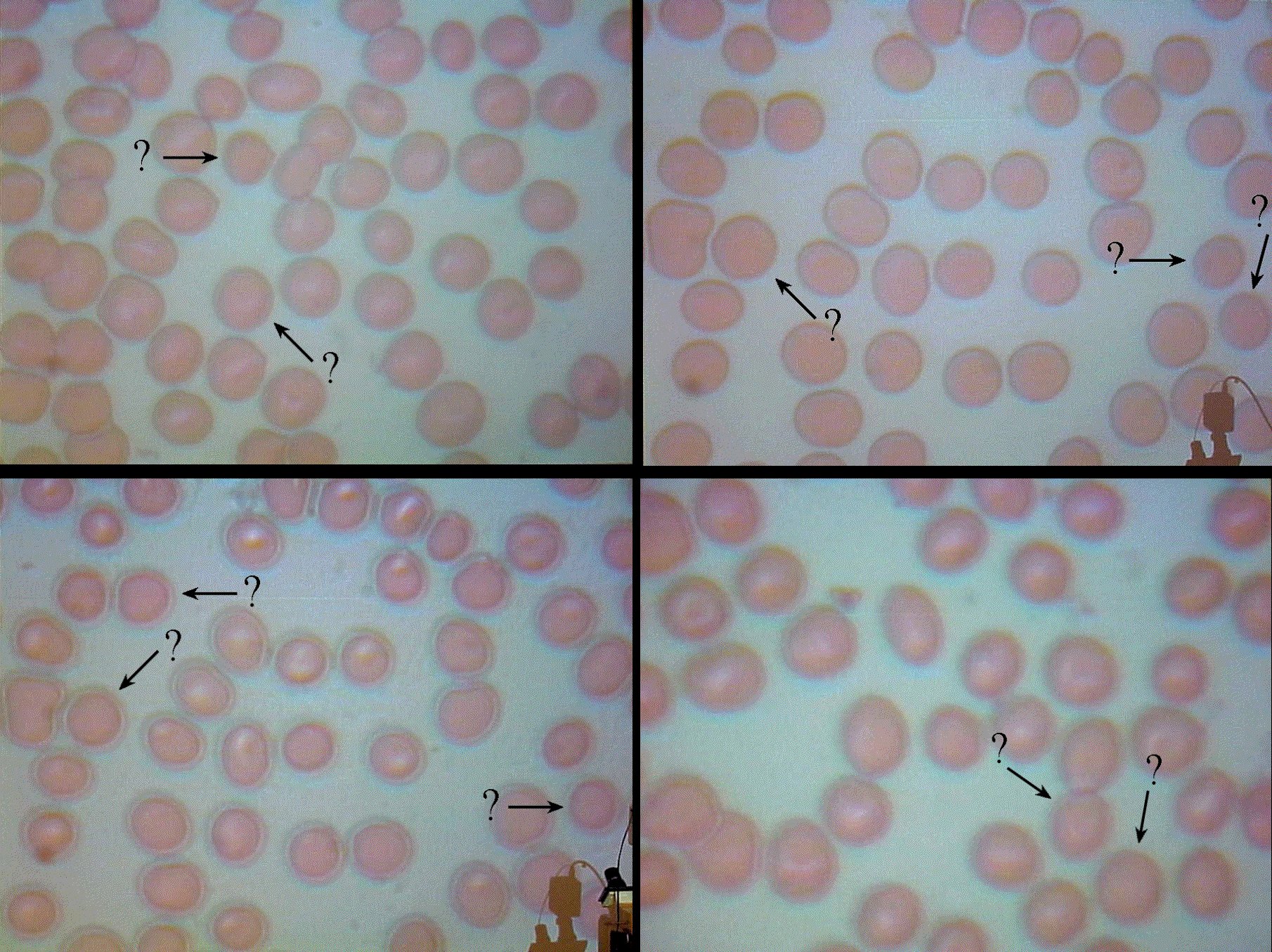
Click on the image for a detailed discussion
|


 Return to My Blood.
Return to My Blood.